Gait Analysis
Gait analysis is a process where a person's manner of walking is compared with CCTV footage of the accused.
It's the systematic study of animal locomotion, specifically human motion, employing observers' eyes and brains and quantifying body movements, body mechanics, and muscle activity.
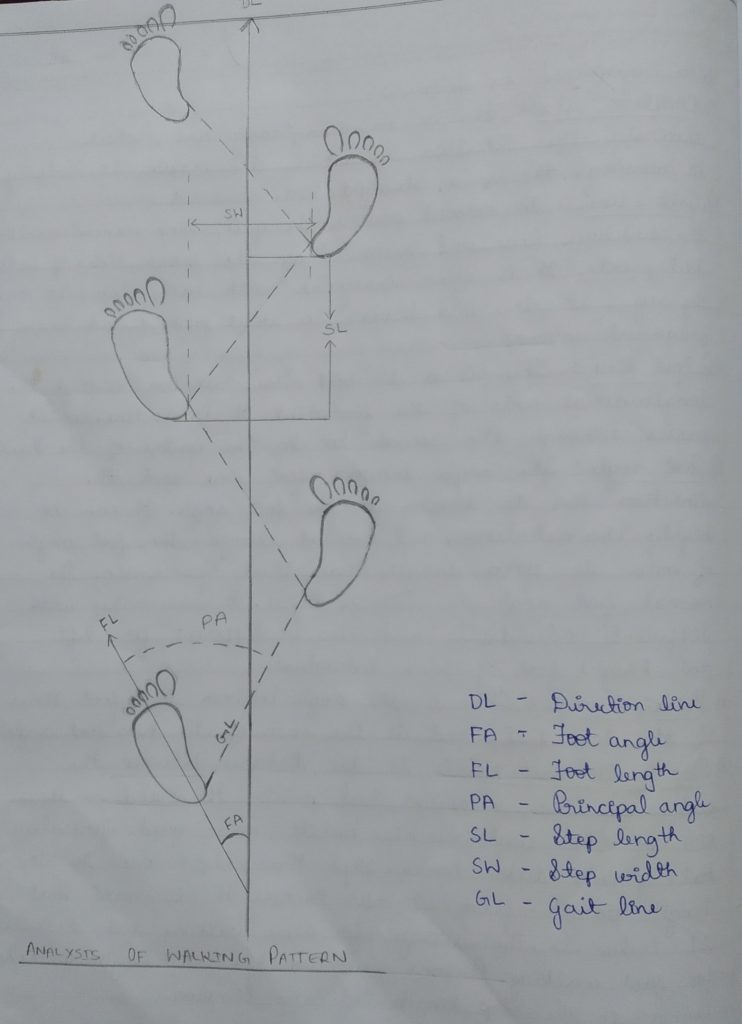
An individual, while walking or running makes a series of impressions or footprints, this is called as a gait pattern.
Gait pattern is created due to the movement of limbs during locomotion. Gait pattern is found to be highly individualistic.
Hence it acts as evidence in solving certain crimes.
Examining and analysing the gait pattern of an individual is very important because it helps to determine age, sex, height of an individual.
Since walking is an unconscious behaviour, it can be used for the identification of an individual.
Gait is a biological characteristic of an individual.
There are several factors that affect gait pattern like personality, footwear of an individual, sex, emotional behaviour, speed of walking, any disorders, age, pregnancy, light conditions.
Gait pattern can be seen in most of the cases like robbery, murder, theft, housebreaking, dacoity, kidnapping, etc.
Gait pattern is the most commonly encountered pattern evidence found in most of the crime scenes and it helps to create a link between crime and criminal.
It also helps to determine the number of suspects involved in the commission of crime.
Directorate of Forensic Science Laboratory (DFSL), Mumbai performed the Gait Analysis
Directorate of Forensic Science Laboratory (DFSL), Mumbai, was established in the year 1958.
It serves as the headquarters of seven Regional Forensic Science Laboratories (RFSL) and five Mini Forensic Science Laboratories (MFSL) in Maharashtra.
It gets 5,000 cyber forensics cases a year.
The DFSL’s main function is to provide scientific opinion on different types of evidential material referred to by the investigating agencies and help the judiciary.
These pieces of evidence act as mute witnesses against the perpetrators and are impartial.
A forensic scientist employed in the laboratory helps police in the collection of the right evidence material from the scene of the crime
DFSL reports were used in numerous high-profile cases, including the 1993 Bombay serial bombings, which killed 260 and injured 1,400.
DFSL provided forensic evidence for the 2006 train and 2011 serial bombs in Mumbai, the 2010 German bakery blast in Pune, and the 26/11 terrorist attacks.
The DFSL office has five divisions – toxicology, biology, DNA, general analytical and instrumentation.
Their areas of expertise cover the full gamut of forensic science — narcotics and explosives, prohibition and excise, ballistics, physics, tape authentication, speaker identification, cyber forensics, and psychology.
The DFSL’s cyber forensic department identifies which digital media (mobile phones, credit cards, hard drives, etc.,) is present at the scene of the crime, and seizes the media.
At the laboratory, the team makes a duplicate copy of the media, authenticates, identifies and analyses its integrity using the latest technology and presents the report in a sealed envelope or as an exhibit
There are certain limitations of gait pattern analysis regarding its admissibility in a court of law.
As gait pattern is affected by various factors it is difficult to identify and confirm a suspect.
It is considered corroborative evidence in the court of law as it does not confirm who is suspect. The gait pattern does not provide conclusive proof in a court of law.
Source: The Hindu

