SEBI set to open commodities to MFs
Why in the news ?
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is to allow mutual funds to participate in the segment while also actively considering allowing derivatives on commodity indices.
More on news
- This comes two months after the regulator made it mandatory for stock derivatives to move to the physical settlement mechanism in a phased manner.
- The proposal for allowing mutual funds and portfolio management services (PMS) in the commodity derivatives segment is awaiting final approval by SEBI.
- SEBI is also actively considering allowing derivatives on commodity indices.
Physical settlement
- A SEBI committee is separately looking into the issue of physical settlement for commodity derivative contracts.
- The Commodity Derivatives Advisory Committee deliberated upon the issue of physical settlement in commodity derivatives and formed a subgroup to look into this specific matter.
- Physical settlement refers to the system where the contract on the day of expiry is settled through the delivery of the underlying commodity instead of the current practice of cash.
- Based on the suggestions of the advisory committee, the regulator is expected to issue a consultation paper before framing the final guidelines.
Warehousing
- The regulator, however, will have to first frame the warehousing guidelines for nonagriculture commodities before going ahead with physical settlement.
- In September 2016, SEBI introduced warehousing norms for agricommodities to ensure that exchanges do not face any default risk while the settlement and delivery of the commodity is assured.
- Equity exchanges BSE and NSE, which plan to start commodity trading from October, asked SEBI to allow co-location in the commodity derivatives segment as well.
What is Derivative ?
- A derivative is a contract between two or more parties whose value is based on an agreed-upon underlying financial asset (like a security) or set of assets (like an index).
- Common underlying instruments include bonds, commodities, currencies, interest rates, market indexes and stocks.
- Generally belonging to the realm of advanced or technical investing, derivatives are used for speculating and hedging purposes. Speculators seek to profit from changing prices in the underlying asset, index or security.
Example :
- Commodity derivatives are used by farmers and millers to provide a degree of "insurance." The farmer enters the contract to lock in an acceptable price for the commodity, and the miller enters the contract to lock in a guaranteed supply of the commodity.
- Although both the farmer and the miller have reduced risk by hedging, both remain exposed to the risks that prices will change.
- While the farmer is assured of a specified price for the commodity, prices could rise (due to, for instance, a shortage because of weather-related events) and the farmer will end up losing any additional income that could have been earned.
- Likewise, prices for the commodity could drop, and the miller will have to pay more for the commodity than he otherwise would have.
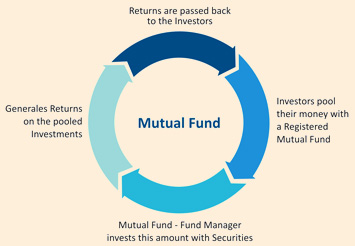
Mutual Funds
- A mutual fund is an investment vehicle made up of a pool of moneys collected from many investors for the purpose of investing in securities such as stocks, bonds, money market instruments and other assets.
- Mutual funds are operated by professional money managers, who allocate the fund's investments and attempt to produce capital gains and/orincome for the fund's investors.
- A mutual fund's portfolio is structured and maintained to match the investment objectives stated in its prospectus.
Source
The Hindu, Investopedia.

